Breast & ColorectalSURGICAL CENTRE
welcome toMaven Surgery
Maven Surgery was established to increase standards of Breast and Colorectal Cancer Healthcare and provide personalized medical services to our patients.
Our centre is helmed by Dr Chong Chee Keong, a dual-fellowship trained surgeon with more than 20 years of experience in treating the top 2 ranked cancers in both men and women.
Our Specialties
A trusted presence in the surgical field with more than 20 years of experience, we cater to a variety of health conditions with empathy, privacy and professionalism.
Comprehensive breast care & surgical treatments for a range of breast cancer conditions.
Specialising in minimally invasive colorectal surgery and treatments for cancers in the colon and rectum.
Expertise in managing a wide range of other conditions including the gallbladder, colorectal, skin and other areas of the body.
Screening
Our clinic caters for comprehensive screening services for breast, colorectal and other general surgical conditions. We provide professional advice to tailor screenings and treatments to conditions.
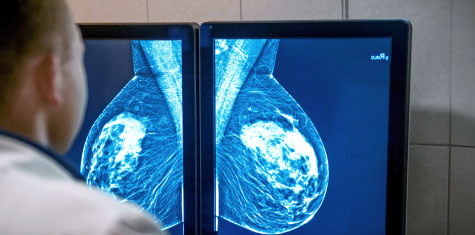
Mammogram
We provide Mammogram Screening for:
- Preventive Care
- Early Detection
- Women aged 40 years old and above
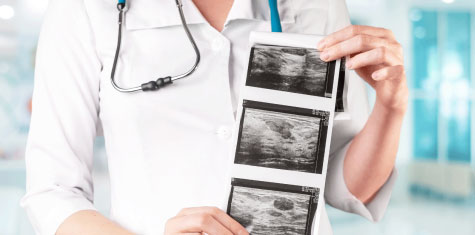
Ultrasound
We provide Ultrasound Screening for:
- Identifying cysts
- Identifying solid masses
- Identifying lymph nodes and abscesses
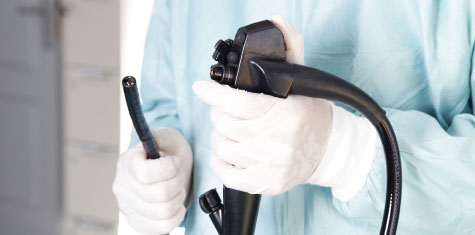
Colonoscopy
We provide Colonoscopy Procedures for:
- Preventive Care
- Early Detection
- Men & women aged 50 years old and above
AboutDr. Chong Chee Keong
Breast, Colorectal and General Surgeon
Dr Chong's dedication to treating Breast and Colorectal cancer patients has led him to start Maven Surgery. As a dual-fellowship trained surgeon with more than 20 years of experience, he is committed to elevate the quality of care for the 2 most common cancers affecting women and men.
Amidst to caring for patients locally, Dr Chong also has a team tailored to serve the needs of his international patients.
View ProfileDr. Chong Chee Keong
MBBS (S’pore), FRCS (Edinburg), FRCS (Glasgow), FAMS (S’pore),
Specialist Accreditation in Intensive Care Medicine, Specialists Accreditation Board,
Medical Director & Senior Consultant
Dr. Chong Chee Keong
MBBS (S’pore), FRCS (Edinburg), FRCS (Glasgow), FAMS (S’pore),
Specialist Accreditation in Intensive Care Medicine, Specialists Accreditation Board,
Medical Director & Senior Consultant
“From Diagnosis to Recovery, We're with You Every Step”
For appointments and enquiries, contact us via form below or call us at (+65) 6355 5285
Mount Elizabeth Novena Specialist Centre
38 Irrawaddy Road #06-33,Singapore 329563
Parkway East Medical Centre
319 Joo Chiat Place #02-05,Singapore 427989
Farrer Park Medical Centre
1 Farrer Park Station Rd #15-13,Singapore 217562
Tel : (+65) 6355 5285
Whatsapp : (+65) 6355 5285
Operating Hours: Monday to Friday: 9:00 AM to 5:00 PM Saturday: 9:00 AM to 1:00 PM Closed on Sundays and Public Holidays